

BLOG
Environmental impact analysis of disc-type sludge thermal drying project
Environmental impact analysis of disc-type sludge thermal drying project
13 November 2024
As an efficient, reliable and energy-saving sludge thermal drying technology, disc drying process technology is of great significance to solving the "sludge siege". Let us pay attention to the pollutants such as water, gas, sound, and slag generated in the sludge disc drying project, and propose corresponding environmental protection measures.
As an industrial large-scale sludge treatment method, the sludge thermal drying process currently plays an important role in solving the "sludge siege". Sludge thermal drying can be divided into direct drying by hot air and flue gas, and indirect drying by steam or heat transfer oil. Different types of process technologies have a great impact on the environment of construction projects. For example, the direct drying technology of hot air and hot flue gas has a low calorific value of hot air and flue gas, and the available heat at 250℃-160℃ is less than 167KJ/Nm3, which is equivalent to 1/10000-1/15000 of the heat released per ton of steam. After drying, a large amount of hot odor is generated, which is difficult to handle, resulting in the operation of the project affecting the occupational health of employees in the factory area and the surrounding area environment.
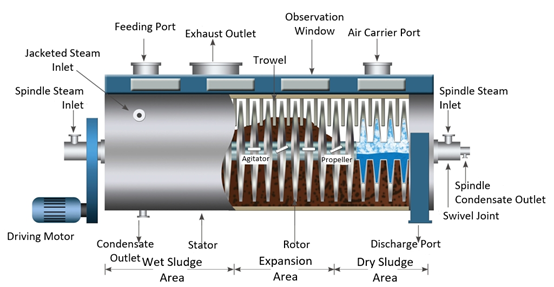
1. Introduction to disc drying process technology
The disc dryer consists of a cylindrical shell and a group of discs with a central penetration. The inside of the disc group is hollow, and the heat medium flows through it, transferring the heat to the sludge indirectly through the disc. The sludge passes between the disc and the shell, receives the heat transferred by the disc, and evaporates the water. The disc group is perpendicular to the hollow axis, and the sludge is pushed and stirred by the feathers. The water vapor formed by the sludge moisture gathers in the dome above the disc and is carried out of the dryer by a small amount of carrier air.
The process flow of the disc sludge drying system is shown in the figure below. The sludge is transported to the entrance of the dryer through the feeding system. The sludge is dried and formed in the dryer at one time. The steam generated during the sludge drying process is discharged from the dryer through the induced draft fan to maintain the micro-negative pressure inside the dryer. The process system is equipped with a pre-dust collector to remove dust. After pre-dust removal, the tail gas enters an indirect water-cooled heat exchanger for condensation, in which the water under the steam condensation is discharged into the sewage pipe network, and the non-condensable gas (mainly some odorous gases) enters the biological deodorization system and is directly discharged after meeting the standards.
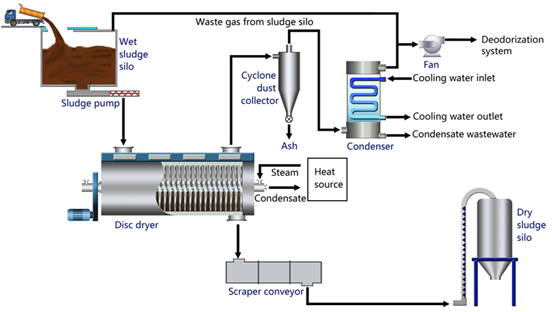
2. Material balance and product link analysis of the process system
Take the single-line 100t/d sludge drying as an example.
In the drying system unit, the wet sludge is generally transported by a screw pump or a screw conveyor. After 1-2 hours of drying and forming in the disc dryer, 3-5mm (60% DS) particles are formed. The dried sludge is transported to the terminal disposal (thermal power plant, garbage power plant, cement plant, etc.) by a screw conveyor. After drying (60% DS), 100t/d of wet sludge produces ~33.3t of dry sludge particles, the volume is reduced, and ~66.7t/d of wastewater will be produced.
While evaporating water, the dryer releases odors and organic waste gases such as methane, ethane, ammonia, and hydrogen sulfide in the sludge, and carries a small amount of dust. The process system is equipped with a dust collector and a condensation system. The final non-condensed waste gas is discharged after passing through the biological deodorization device. In this process, a certain amount of wastewater and waste gas will be generated.
3. Wastewater
The condensed wastewater of tail gas ~ 66.7t of wastewater was sampled and tested by the condensed wastewater of the Jiaxing sludge disc thermal drying project (heat medium: water vapor, 0.5Mpa, 153℃).
The test results show that the biodegradability of the dried condensed wastewater is good, but the ammonia nitrogen index is high. The source of pollutant concentration in wastewater is not only related to the source of sludge, but also related to the temperature of the drying heat medium. Changing the working conditions, the thermal drying experiment of two sludge samples of Jiaxing municipal sludge showed that under 160℃, the COD of condensed wastewater was 410.0-710.4mg/l and the pH was 6.84-7.63.
The amount of dried condensed wastewater is small. The construction of drying projects in sewage treatment plants can be directly connected to the sewage treatment system. Other project sites need to add sewage treatment facilities. For example, in thermal power plants or cement plants, the condensed wastewater treatment process is: wastewater → regulating tank → pump → heat exchanger → A/O tank → reaction sedimentation filter tank → disinfection tank → recycled water utilization. The generated sludge is filtered through a plate and frame filter press and returned to the dryer for treatment. Due to the good biodegradability of the wastewater, it meets the industrial recycled water standard and the treatment cost is ~3 yuan/ton of wastewater.
4. Waste gas
The waste gas source of the disc drying project is the ventilation of the drying workshop and the tail gas of the drying process. The ventilation rate of the drying plant is generally 8-10. After collection, it is treated by biological deodorization to meet the secondary emission standard of the "Emission Standard of Malodorous Pollutants". Process waste gas is the main source of pollution in the construction project.
The main components of the tail gas of the drying process are water vapor, a small amount of dust, hydrogen sulfide, ammonia, methane and other organic waste gases and malodorous gases. The amount of dust in the sludge drying process is closely related to the degree of drying. When the sludge is dried to 60% DS, the dust content is almost not generated. When it is dried to 70% DS, the amount of dust begins to increase. When it is dried to 90% DS, the amount of dust is large and can reach 30.5g/Nm3. It is generally believed that the process system is safe if the sludge dust concentration is within 60g/Nm3. Of course, this indicator is also related to the conditions such as the concentration of combustible gas, temperature, pressure, oxygen content, and ignition energy. The dust collector efficiency can generally reach more than 95%, and the dust collector collects ash and mixes it with dry sludge particles for final disposal. The non-condensable gas is analyzed for composition and concentration online by the GASMET-DX4000 flue gas analyzer. The concentrations of ammonia, organic acid, methane and propane are all near the instrument's minimum detection limit.
Some pollutants enter the condensation wastewater after condensation, and the pollutant concentration of the waste gas is reduced. The condensation of pollutants into the wastewater is related to the nature of the gas. Finally, the process non-condensable gas finally enters the biological deodorization device. The biological deodorization device generally uses internal gas to pass through the washing tower in reverse (from bottom to top). The circulating water pump pumps the circulating liquid from the bottom circulating water tank to the upper part of the packing layer of the packing tower. The spiral nozzle is used to evenly spray the circulating liquid on the packing layer of the tower. The fan at the rear of the packing tower is used as the power. When passing through the packing layer, the circulating liquid absorbs the waste gas part that is soluble in the circulating liquid; the non-condensable passes through the demisting layer and the connecting pipe to the fan and is discharged through the discharge chimney.
5. Waste residue
The waste residue produced by the disc drying process is mainly dry sludge particles, which have a certain calorific value and are directly related to the source of the sludge. Dried sludge particles can be used as low-organic energy in thermal power plants, waste power plants, and cement kilns for final disposal, or as carbon soil.
If the dried sludge enters the cement kiln for disposal, first, the material temperature in the rotary kiln is 1450-1550℃, and the gas temperature is higher, reaching 1700-1800℃. At this high temperature, the organic matter in the sludge is completely decomposed. Secondly, the large-scale cement production system has a large-scale heat capacity, allowing moderate fluctuations in the quantity and quality of the incoming materials. The ash content of 100 tons of sludge is only about 10 tons, which is only 0.1-1% for a daily output of 5,000-10,000 tons of cement clinker. Therefore, the scale of solid waste utilization can be far greater than the processing capacity of existing professional equipment. Thirdly, there is no waste residue discharge. The cement kiln inputs raw materials, coal powder and dried sludge, and outputs cement clinker. The sludge resources can be recycled, truly achieving zero solid waste emissions, and its economic and environmental benefits are better.
After drying, the sludge is finally disposed of in the waste incinerator system. The contribution rate of sludge to the pollutants of the waste incineration system is small, and the impact on the environment is small.
If the dried sludge is used as carbon soil, the water in the sludge is evaporated after disc drying, and the 100-120℃ environment can sterilize and disinfect, preventing pathogenic bacteria and microorganisms from entering the soil environment. In addition, the disc thermal drying process does not change the inherent components in the sludge, does not increase the content of S, Cl, and heavy metals in the sludge, and avoids secondary pollution to the soil and groundwater environment.

6. Noise
The main equipment in the disc drying system includes disc dryer, wet sludge silo, sludge conveying pump, etc., and its noise meets the Class II standard of the "Industrial Enterprise Boundary Noise Standard" (GB12348-90), and the environmental impact of noise is small.
7. OthersDioxins produced by sludge drying and incineration are sensitive issues of environmental impact concern for construction projects. According to research at home and abroad, in the test of mixed combustion of coal and garbage, it was found that S/Cl=1~5 can greatly reduce the emission of dioxins. When S/Cl=10 in the fuel, 90% of dioxin generation can be inhibited.



