

BLOG
Exploration of Drying and Incineration Process
Exploration of Drying and Incineration Process
25 December 2024
With the acceleration of urbanization and the continuous development of industrial production, the generation of sludge has been increasing steadily. Sludge contains a large amount of organic matter, heavy metals, and other harmful components, which pose a potential threat to the environment if not properly treated. Therefore, sludge treatment and disposal have become crucial tasks in urban construction and environmental protection. Currently, sludge drying and incineration, as an effective sludge treatment method, have been widely applied both domestically and internationally.
The principles guiding current sludge treatment and disposal are "reduction, stabilization, harmlessness, and resource recovery," which are important measures for realizing circular economy and ecological civilization construction. They represent significant goals for the development of sludge treatment and disposal technologies and serve as the driving force and direction for future advancements.
However, regarding the current methods of sludge disposal, land use has seen illegal dumping and landfilling in the name of "soil improvement." Brick factories have ceased sludge disposal due to limited markets for sludge-based building materials and the lack of pollution prevention measures. Therefore, comprehensively speaking, sludge incineration remains the mainstream disposal process at present.
1. Forms and Characteristics of Sludge Incineration
There are three forms of sludge incineration:
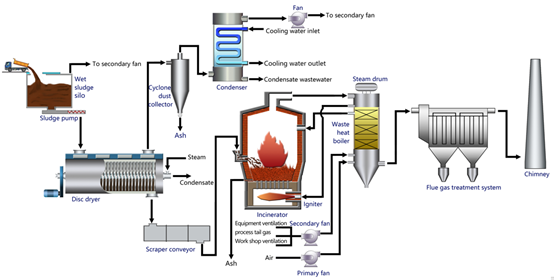
(1) Drying + Co-incineration: The mixing ratio of dried sludge is approximately 7% to 8%, mostly involving technical upgrades in power plants, with a short duration and low investment costs, requiring no planning by large design institutes.
(2) Drying + Independent Incineration: Large-scale sludge treatment and disposal, long duration, high investment costs, requiring planning by large design institutes.
(3) Direct Co-firing of Wet Sludge: The mixing ratio of wet sludge is less than 5%, significantly affecting boiler efficiency and the stability of the incineration system.
There are many application cases of co-drying and co-incineration of sludge in waste incineration plants and thermal power plants both domestically and internationally.
- Co-incineration of Dried Sludge with Power Plants
In terms of energy, high-temperature condensate from saturated steam after condensation can be treated and used as boiler makeup water, enabling the recycling of thermal energy. At the same time, dried sludge also serves as an auxiliary fuel to supplement the system's energy.
In terms of utilities, dried sludge exhaust can be treated using the power plant's exhaust gas treatment system, eliminating the need for a new and costly exhaust gas treatment system. Existing power plant facilities can be utilized for other public works.
- Advantages of Co-disposing Sludge with Power Plants
Co-disposing sludge with power plants offers significant advantages in terms of cost, environmental protection, efficiency, and energy conservation.
(1) Low investment costs and short construction duration: The incineration system and utilities are fully equipped, resulting in cost savings of 10% to 15%.
(2) Thorough disposal without secondary pollution: Organic matter and pathogens are thoroughly disposed of, and heavy metals are highly solidified.
(3) High efficiency and large capacity: Harmful substances are rapidly converted, with high treatment efficiency and a reduction rate of up to 93% (for sludge with an 80% water content).
(4) Energy coupling, energy conservation, and emission reduction: Low-grade steam utilization, energy recycling, and sludge calorific value utilization contribute to energy conservation and emission reduction.
- Factors Influencing Co-disposing Sludge with Power Plants
There are four main factors influencing co-disposing sludge with power plants:
Firstly, the water content of sludge. Generally, the water content for sludge incineration is controlled between 30% and 40%.
Secondly, the mixing ratio of sludge. Considering current standards and actual operational parameters, the mixing ratio of sludge is below 8%.
Thirdly, wear, corrosion, and slagging of boiler equipment. Modifications are required to the heated tail sections of coal-fired power plant boilers, incorporating corrosion-resistant and wear-resistant materials.
Fourthly, the impact on pollutant emissions. Enhance tracking and monitoring of flue gas and other pollutant emissions, and based on actual project operations, increase dioxin and mercury reduction facilities.
Advantages of Co-disposing Sludge with Power Plants in Energy Conservation and Carbon Reduction. Dried wet sludge contains a certain calorific value. Wet sludge with a water content of 35% has a calorific value of approximately 1,300 kcal/kg, which can replace pulverized coal fuel to reduce CO2 emissions. Calculations show that incorporating 1 ton of sludge can save 0.152 tons of standard coal and reduce CO2 emissions by 0.41 tons.

TIC Technology Co., Ltd., addressing industry pain points and customer needs, breaks the traditional sludge drying process route and adopts a sludge drying and incineration process for sludge reduction and harmless treatment, achieving a reduction in water content to below 30%. At the same time, generating electricity through sludge incineration saves nearly 10,000 tons of standard coal annually, with significant energy-saving effects, realizing dual benefits in resource utilization and operational costs.



