

BLOG
Factors Affecting the Effect of Sludge Drying
Factors Affecting the Effect of Sludge Drying
05 February 2025
In the process of sludge treatment, sludge drying is a crucial step that significantly influences the subsequent disposal and utilization of sludge. The efficiency and quality of sludge drying are affected by multiple factors. Understanding these factors is of great importance for optimizing the sludge drying process, improving energy efficiency, and reducing costs. This article will discuss the key factors that impact the effect of sludge drying.
Sludge Characteristics
Moisture Content
The initial moisture content of sludge is one of the most fundamental and decisive factors affecting the drying process. High - moisture sludge is a major challenge in the drying operation. Typically, sludge from wastewater treatment plants has an initial moisture content ranging from 80% to 99.5%. For instance, when the moisture content of sludge is as high as 95%, nearly all of its weight is composed of water. To achieve a practical dryness level suitable for further disposal or utilization, such as reducing the moisture content to around 30%, an enormous amount of water needs to be evaporated.
According to research, increasing the initial moisture content of sludge by 10% can lead to a 30 - 50% increase in the drying time and energy consumption. As shown in Figure 1 below, it clearly demonstrates the relationship between the initial moisture content of sludge and the drying time. The higher the initial moisture content, the longer the drying time required. High - moisture sludge also exhibits greater viscosity, which creates a significant barrier to heat transfer. The viscous nature of the sludge restricts the movement of heat through it, impeding the efficient evaporation of water. Additionally, the high viscosity makes it difficult for the sludge to flow smoothly within the drying equipment, potentially causing operational disruptions and even equipment blockages.
| Initial Moisture Content (%) | Drying Time (hours) |
| 80 | 10 |
| 90 | 15 |
| 95 | 20 |
Figure 1: Relationship between Initial Moisture Content of Sludge and Drying Time
Composition
The composition of sludge is a complex and multi - faceted aspect that plays a vital role in the drying process. Organic matter in sludge, including proteins, fats, and carbohydrates, undergoes various decomposition and chemical reactions during drying. High - organic sludge, which contains a large proportion of these substances, often becomes sticky during the drying process. This stickiness can cause serious problems such as agglomeration, where the sludge particles clump together, reducing the effective surface area for heat transfer and water evaporation. Moreover, the sticky sludge can clog the drying equipment, leading to frequent maintenance and cleaning requirements. This not only interrupts the normal operation of the drying process but also significantly increases the maintenance cost of the equipment.
In addition to organic matter, the presence of certain inorganic substances in sludge, such as heavy metals and salts, also has a profound impact on the drying behavior. Heavy metals, like lead, mercury, and cadmium, can alter the physical and chemical properties of sludge. They may form complex compounds with other components in the sludge, affecting its thermal stability and the rate of water evaporation. For example, some heavy metals can catalyze certain chemical reactions during drying, which may lead to the release of harmful gases or the formation of new, less - desirable substances. Salts in sludge, on the other hand, can cause corrosion of the drying equipment under specific conditions. When the sludge contains high levels of chloride salts, for instance, it can react with the metal components of the drying equipment in the presence of moisture and heat, leading to the degradation of the equipment and reducing its lifespan.
Particle Size and Shape
The particle size and shape of sludge have a significant and direct impact on the drying rate. Smaller and more regular - shaped particles possess a larger specific surface area relative to their volume. This increased surface area exposes more water molecules to the heat source, facilitating faster heat transfer and water evaporation. Research has shown that sludge particles with a diameter of less than 1 mm can be dried up to 50% faster than particles with a diameter of 5 - 10 mm. When the sludge particles are uniform in shape, such as spherical or cubic, the heat distribution within the particles is more even, ensuring a more efficient drying process.
Conversely, large and irregularly - shaped particles have a smaller specific surface area relative to their volume. Water inside these particles needs to travel a longer distance to reach the surface and evaporate. This extended diffusion path for water molecules prolongs the drying time. For example, untreated sludge with large clumps may take several times longer to dry compared to sludge that has been properly pulverized or treated to reduce particle size. In addition, irregular - shaped particles can cause uneven flow and mixing within the drying equipment, leading to inconsistent drying results. As depicted in Figure 2, it illustrates the different drying rates of sludge with varying particle sizes.
| Particle Size (mm) | Drying Rate (kg/h) |
| < 1 | 10 |
| 1 - 5 | 6 |
| 5 - 10 | 4 |
Figure 2: Relationship between Particle Size of Sludge and Drying Rate
Drying Process and Equipment
Drying Technology
Different drying technologies have distinct drying mechanisms and characteristics, which directly affect the drying effect. Direct drying technology involves the direct contact between the hot medium (such as hot air or flue gas) and the sludge. This method has a high heat transfer efficiency because the heat is directly transferred to the sludge. However, it may also lead to uneven heating and local overheating, which can cause the deterioration of sludge quality. Indirect drying technology, on the other hand, transfers heat to the sludge through a heat exchanger. This approach allows for better control of the drying temperature, reducing the risk of overheating. But the heat transfer efficiency is relatively lower compared to direct drying. The comparison of the two drying technologies is presented in Table 1.
| Drying Technology | Heat Transfer Efficiency | Temperature Control | Risk of Overheating | Impact on Sludge Quality |
| Direct Drying | High | Difficult | High | May cause deterioration |
| Indirect Drying | Relatively lower | Easy | Low | Less impact |
Table 1: Comparison of Direct and Indirect Drying Technologies
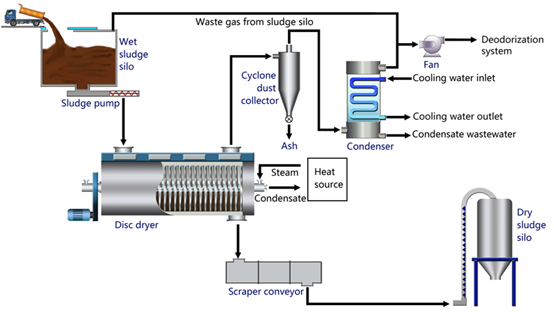
Equipment Performance
The performance of the drying equipment is crucial for the success of the drying process. The design and structure of the dryer, such as the size of the drying chamber, the type of heating element, and the ventilation system, all have a significant impact on the drying effect. For example, in a rotary drum dryer, the rotation speed of the drum, the inclination angle, and the design of the lifting plates inside the drum affect the residence time of the sludge in the dryer, the mixing degree of the sludge, and the uniformity of heat distribution. A well - designed dryer can ensure that the sludge is evenly heated and dried, while a poorly designed one may result in incomplete drying or uneven drying of the sludge.
Operating Conditions
Temperature
The drying temperature is a key operating parameter. Generally, increasing the drying temperature can accelerate the evaporation rate of water, thereby shortening the drying time. However, excessively high temperatures can lead to problems such as the burning of sludge, the release of harmful gases, and the damage of the drying equipment. Different types of sludge have their optimal drying temperature ranges. For example, some sludges with high organic matter content may require relatively lower temperatures to avoid excessive decomposition and the production of unpleasant odors. Figure 3 shows the relationship between drying temperature and drying time for a certain type of sludge.
| Drying Temperature (°C) | Drying Time (hours) |
| 80 | 12 |
| 100 | 8 |
| 120 | 6 |
Figure 3: Relationship between Drying Temperature and Drying Time for a Certain Type of Sludge
Residence Time
The residence time of sludge in the drying equipment is directly related to the degree of drying. If the residence time is too short, the water in the sludge may not have enough time to evaporate completely, resulting in insufficient drying. Conversely, if the residence time is too long, although the drying degree can be improved, it will reduce the production efficiency of the equipment and increase energy consumption. Therefore, it is necessary to determine the appropriate residence time according to the characteristics of the sludge and the requirements of the drying effect.
Airflow Rate
Adequate airflow is essential for the removal of evaporated water vapor from the sludge surface. A good ventilation system can quickly carry away the water vapor, reducing the humidity around the sludge and creating a favorable environment for continuous water evaporation. If the airflow rate is too low, the water vapor will accumulate around the sludge, reducing the driving force for water evaporation and slowing down the drying process. On the other hand, if the airflow rate is too high, it may carry away a large amount of heat, reducing the thermal efficiency of the drying system.
Environmental Factors
Ambient Humidity
The ambient humidity has a significant impact on the drying rate of sludge. When the ambient humidity is high, the difference in water vapor partial pressure between the sludge surface and the surrounding environment is small. This reduces the driving force for water evaporation from the sludge, resulting in a slower drying rate. In contrast, in a dry environment, the water vapor partial pressure difference is large, which promotes the evaporation of water from the sludge. For example, in a humid tropical region, the sludge drying process may take longer compared to a dry desert area under the same drying conditions.
Altitude
Altitude affects the atmospheric pressure, which in turn affects the boiling point of water. At high altitudes, the atmospheric pressure is lower, and the boiling point of water is also lower. This means that water can evaporate more easily at a lower temperature, which is beneficial to the sludge drying process to some extent. However, at high altitudes, the air is thinner, which may affect the heat transfer efficiency and the performance of the ventilation system in the drying equipment.
In conclusion, the effect of sludge drying is influenced by a variety of factors, including sludge characteristics, drying process and equipment, operating conditions, and environmental factors. By comprehensively considering and optimizing these factors, it is possible to improve the efficiency and quality of the sludge drying process, achieving better economic and environmental benefits.



